In today’s digital dental technology, 3D printing and milling are two of the most common methods for manufacturing full dentures. Both have their strengths, and choosing the right technique depends on the case, cost, and desired outcome.
3d printing
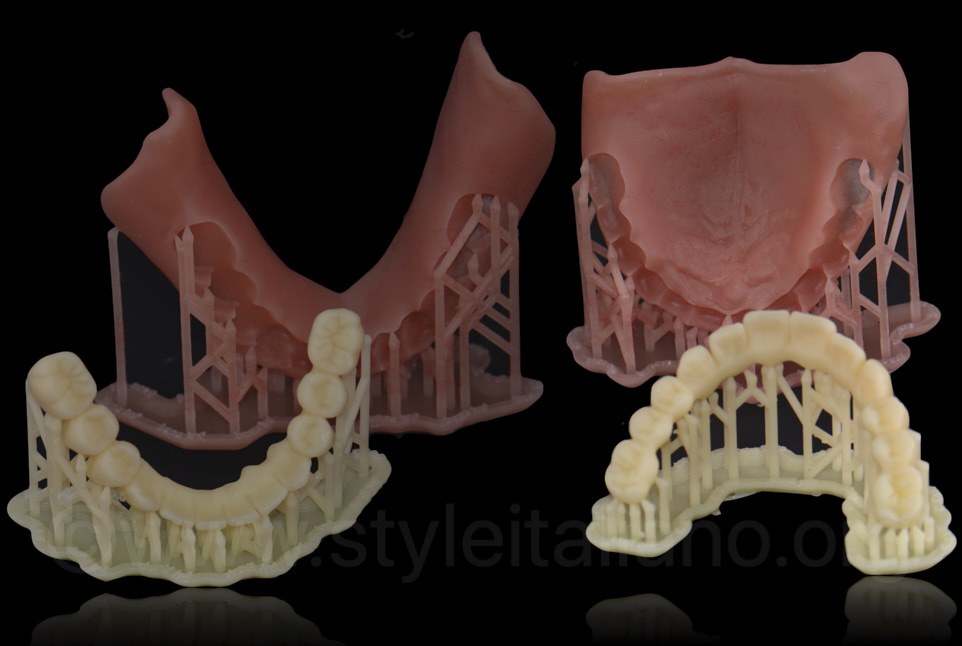
A title
Image Box text
MILLING
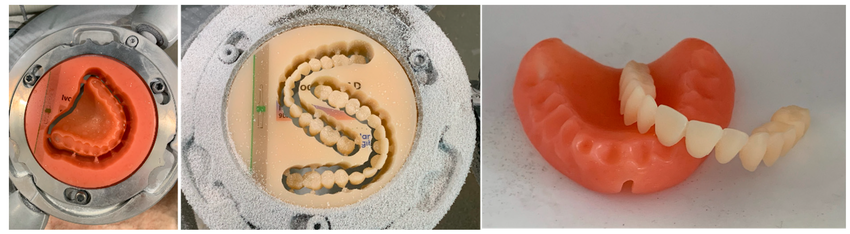
A title
Image Box text
1. Accuracy & Fit
3D Printing: Accuracy is improving significantly with new printers and resins, but fit can be slightly affected by post-curing, resin shrinkage, or printer calibration.
Milling: Provides excellent precision since dentures are carved from a pre-polymerized puck. The material is stable with very low shrinkage, leading to highly accurate fits.
2. Strength & Durability
3D Printing: Printed dentures are more prone to wear and fractures, though new high-strength printable resins are narrowing the gap. Best for interim or economy dentures.
Milling: Milled dentures are generally stronger because the material block is dense and fully cured. This makes them ideal for long-term dentures.
3. Aesthetics
3D Printing: Offers more flexibility in tooth and base designs, with multi-layer or multi-material printing on the rise for better esthetics.
Milling: Provides consistent shade and translucency but limited to available puck colors. Layering or characterization is possible but more labor-intensive.
4. Efficiency & Cost
3D Printing: More cost-effective since there is minimal material waste. Printing multiple dentures at once saves time, making it faster for volume production.
Milling: Higher material cost due to waste from carving the block, and milling machines require regular maintenance. Slower for full arch jobs.
5. Best Use Cases
3D Printing: Economical dentures, immediate or temporary dentures, and faster turnaround when multiple cases need to be produced.
Milling: Long-term, premium quality dentures with maximum strength and precision.
👉 Conclusion:
Both methods play an important role in modern denture fabrication. Milling is the gold standard for durability and precision, while 3D printing is the future of speed, flexibility, and scalability. Many labs today are combining both approaches to deliver the best outcomes for patients.
